Corneal Collagen Cross-Linking (CXL) is a non-surgical procedure used to strengthen the cornea. This treatment utilizes riboflavin (vitamin B2) combined with UV-A light to increase the bonding between collagen fibers in the cornea. CXL is performed to stabilize corneal structure, prevent disease progression, and reduce the risk of serious visual impairment.
When Is Cross-Linking Needed?
Keratoconus: Thinning and progressive bulging of the cornea into a cone-like shape.
Post-LASIK Ectasia: Corneal weakening and instability after refractive surgery.

Corneal thinning or irregularity, Gradual thinning and deformation of the cornea.

Patients at high risk individuals with a high risk of keratoconus progression.
How Is Cross-Linking Performed?
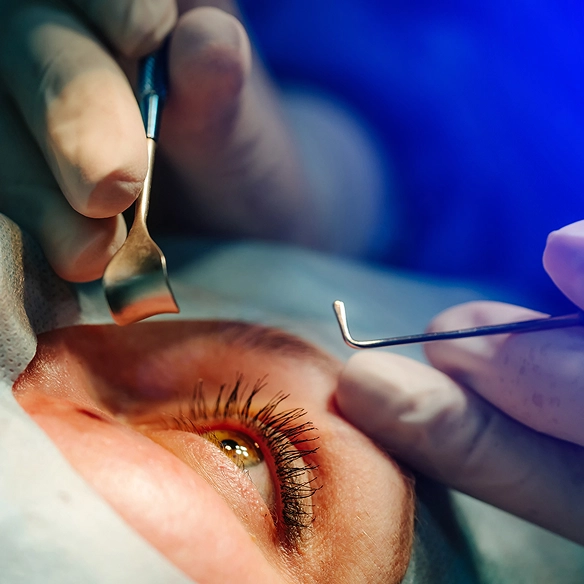
Anesthetic eye drops are applied to numb the eyes.
Riboflavin drops are instilled onto the corneal surface.
UV-A light is directed to the eyes to initiate the cross-linking process.

The procedure lasts approximately 30–60 minutes.

After the procedure, patients will wear a soft bandage contact lens and receive eye drops to support healing.

Benefits of Cross-Linking
- Slows or stops the progression of keratoconus.
- Reduces the likelihood of future corneal transplantation.
- Improves corneal stability.
- Minimally invasive and does not require major surgery.
- Can be performed in teenagers when symptoms begin to appear.
FAQ
No. The procedure is performed using anesthetic eye drops and involves minimal discomfort.
It does not cure the condition, but it is highly effective in slowing down or stopping its progression.
As early as possible once keratoconus is detected, especially in teenagers and young adults.
Side effects are generally mild, such as dry eyes, temporary glare, or mild discomfort for a few days.
Free From Glasses and Contact Lenses, Life Becomes Easier
Register now and consult directly with our eye specialists for the best treatment for you.











